Release date: June 24, 2022
Deliverable Summary:
Data arriving to Portal will be evaluated for analyzability.
Definition:
When data arrives into the Eureka AI platform, from any data acquisition source, that data should be screened for data quality. Data quality includes identification of machine running in compliance with test operating conditions, complete data package of all asset locations, data is not flatlined, and data does not have overloaded/overheated signal or ski-slope. Data that meets the criteria for data quality will be passed for automated analysis per any service level agreement. Data that does not meet criteria for data quality is annotated and reported as such.
Usage:
The objective of the Data Quality Check is to flag data which appears to be unanalyzable including the reason why. Upon running the automated diagnostic engine, an analyst will be presented a result from the Data Quality Check if there are any discrepancies in the vibration data.
Analyst can then steer the next steps as required, such as rejecting the data, requesting retest, etc.
Release Information and Examples:
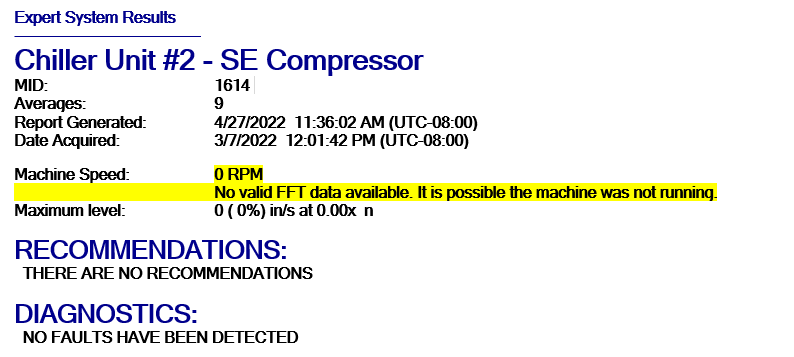
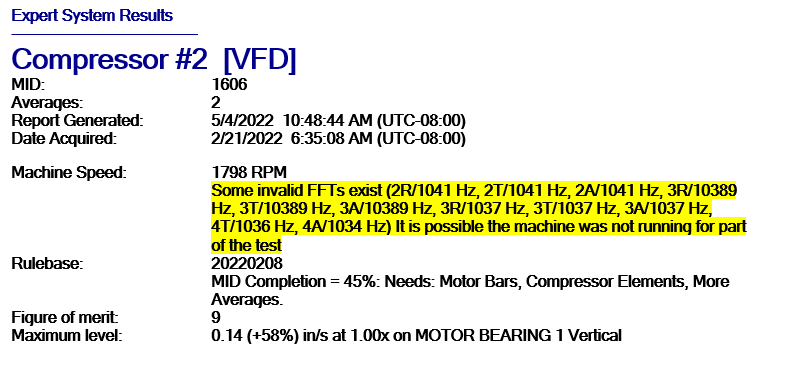
Flatline Detector:
The flatline detection scheme separates a machine into three operating states. The first of which is where the machine is running normally during the entirety of the data acquisition process. The second case is when the machine is non-operating for the entirety of the test. And the final case is where the machine is operating at the beginning of the data acquisition but turns off at some point during the acquisition and so provides incomplete spectra to EADS.
The results of the Data Quality check will appear in the Expert System Result. The Data Quality Check result does not appear in the Reviewed Analyst Result nor the PredictivePortal.
See highlighted section below:
Additional Improvements to Automated Diagnostics
Fmax Validation
A division by zero error is reported in the EA results screen when the measurement Fmax is less than 0.95 orders of the prime mover shaft rate. This error has been addressed by discarding spectra that meet this condition while keeping the remainder. A message is presented to the user indicating which pickup locations were flagged as having too low of an Fmax.
Random Impacting
During characterization of the type of Impact Demod, a subroutine checks to see if a particular Impact Demod waveform appears to be synchronous, non-synchronous, or random. Improvements were made to ensure the type of impact Demod maintains the random = true after failing the synchronous and non-synchronous checks.
Comments